Kerberos Introduction
skohan / March 2022
Quick introduction to kerberos and how it works.
Used for Security and Authentication
KDC (Key Distribution Center) has
- AS (Authenitcation server)
- TGS (Ticket Granting server)
Working
(SK1) (SK1, SK2)
AS <---Database---> TGS
\ /
\ /
\ /
\ /
\ /
\ /
Client <-------------------> File Server (For Example)
(SK2)
-
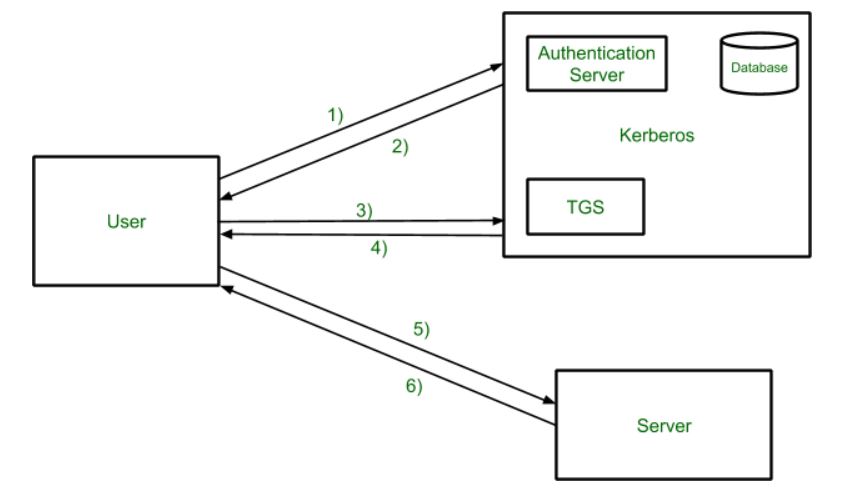
Client wants to access perticular files on file server.
-
Client sends request to AS with userId and request info encrypted with their password. It is partially enctrypted to access userId only.
-
AS search up userId and fetches password to decrypt request. After veryfing client, it sends TGT (Ticket Granting Ticket) encrypted with SK1 (Secret Key 1). This secret key is shared between AS and TGS.
-
Client sends TGT along with request (like to access file server or any other service) to TGS. TGS decrypts the TGT with SK1 and validates the request.
-
TGS issues client a token encrypted with SK2 (Secret Key 2). TGS and File server shares same secret key.
-
Client sends request to File server with token which can be decrypted by using SK2. Token is valid for some amount of time.
Limitation:
- Does not work well in timeshared environment
- All passwords with single key
Architecture diagram
References
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_44CHD3Vx-0
Resources
Kerberos on Ambari docker image
https://blog.spacepatroldelta.com/a?ID=01000-21018c30-1fbe-4940-b2e1-f5e1d206a8e0
https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/siffs/2.0.3?topic=nodes-enabling-kerberos-hdp
https://kylo.readthedocs.io/en/v0.10.0/developer-guides/KerberosInstallationExampleHDP2.4.html